Sunday, September 17, 2017
Level With Me, Half-Life 2, complete!
I've just finished playing through all of Half-Life 2 on my level design streaming show, Level With Me. Much like with my playthrough of Half-Life 1, I've played through this sequel several times already, and I thought I knew it pretty well -- but there were still sequences where I was surprised, impressed, or disappointed.
There were several main themes throughout this playthrough:
1. The current version of Half-Life 2, the only one now available on Steam, has been poorly updated and maintained. When Valve added HDR lighting to Source Engine 1, someone dutifully went through Half-Life 2 and updated all the maps -- but that process only involved recompiling the maps with HDR lighting. That broke several things: there are no LDR lightmaps (it's impossible to play Half-Life 2 without HDR now), and the unchanged settings are poorly calibrated for HDR, often being too bright / too dark / with lots of halo-y hotspots everywhere. If you want to play a better version of Half-Life 2, I recommend the Half-Life 2 Update mod, which fixes a lot of these issues.
2. Another frequent theme has been how Half-Life 2 keeps mixing itself up; one chapter is a horror survival segment, and then 2 minutes later the next chapter is a road trip driving section. This is pretty unusual in 2017, where AAA action games usually feel more consistent, systemic, and homogeneous. (Of the big franchises, maybe only Call of Duty maintains this roller coaster setpiece structure.) You could argue that Half-Life 2 sort of tries to do 10 different things, and doesn't really excel at any of them. Or on the flip-side, maybe the Valve of 2000-2004 was really impatient and bursting with ideas, and in the end, executes all of these ideas decently enough.
3. Rugs!!!
Check out the full Level With me archived playlist for Half-Life 2 on YouTube, or watch future broadcasts live on Twitch.
Thursday, September 14, 2017
How to Graybox / Blockout a 3D Video Game Level
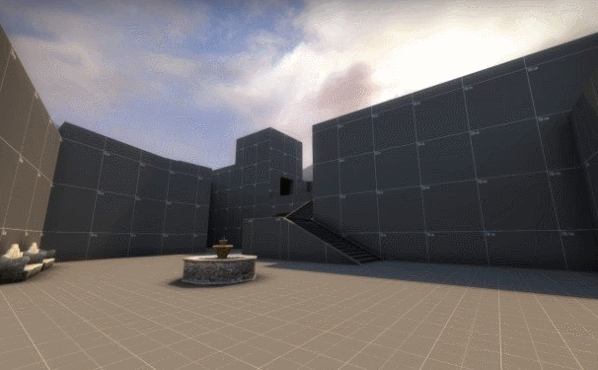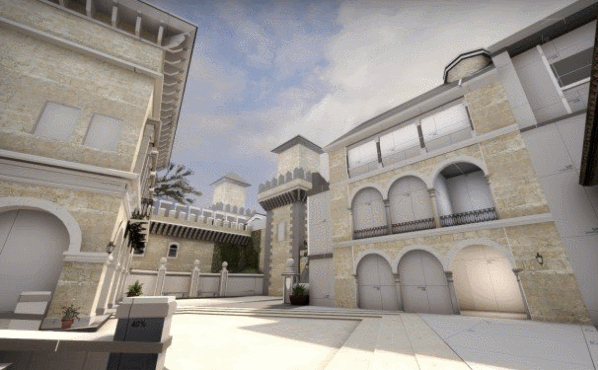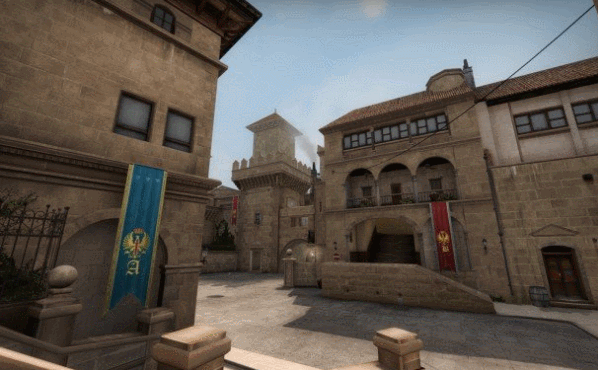 |
| from de_crown, by FMPONE and Volcano |
UPDATE, 11 NOVEMBER 2021: this blog post is OK, but I would recommend reading the "Blockout" page in my free online work-in-progress level design book instead.
ORIGINAL POST:
While planning a level design class, I googled for a good article about blocking-out or grayboxing a 3D level design prototype. I didn't really find one that actually went into "how" you might actually go about grayboxing a level, so I guess I have to write it.
Grayboxing is a level design practice where you build a rough block-out version of your level using blocks (usually gray boxes) so that you can iterate and test the layout as soon as possible. Almost every 3D game engine has some sort of box primitive tool -- if you know how to use that, then you can graybox.
Before you graybox, you must make sure you've established a general game design direction. You should generally know how this level might fit into your game or workflow. There's no point in grayboxing if you don't even know what the player should be doing, or what this level is supposed to convey. Is the level supposed to be easy or hard? Does it focus on combat or non-combat? Should it feel scary or safe? Level design must always exist in the context of a larger game design, or else you're just wasting your time.
Then, open up your 3D game engine, and let's start laying down some boxes...
Grayboxing is a level design practice where you build a rough block-out version of your level using blocks (usually gray boxes) so that you can iterate and test the layout as soon as possible. Almost every 3D game engine has some sort of box primitive tool -- if you know how to use that, then you can graybox.
Before you graybox, you must make sure you've established a general game design direction. You should generally know how this level might fit into your game or workflow. There's no point in grayboxing if you don't even know what the player should be doing, or what this level is supposed to convey. Is the level supposed to be easy or hard? Does it focus on combat or non-combat? Should it feel scary or safe? Level design must always exist in the context of a larger game design, or else you're just wasting your time.
Then, open up your 3D game engine, and let's start laying down some boxes...
Thursday, September 7, 2017
On "Tacoma" by The Fullbright Company
This post spoils some of Tacoma and Sleep No More.
Tacoma is a sensible design progression from Gone Home. How do you expand upon the audio diary design and walking mechanics? The Fullbright Company decided to pair a dynamic holographic drama with some zero gravity movement. Unfortunately, the zero-G movement ended up making environmental storytelling more difficult so they had to scale it back (no tables or chairs; no objects at rest) and I also suspect it risked alienating a fan base that cares less about gamer-y traversal puzzles. So, that leaves all the focus on the holographic drama sequences.
Many commentators describe Tacoma as a virtual adaptation of the NYC immersive theater installation "Sleep No More" because both experiences involve wandering around a large dense environment and encountering short dramatic scenes of characters performing with each other... and then the characters split-off and you have to choose who to follow and listen to.
I think this is a telling comparison, because it also suggests the ways in which Tacoma's formal narrative structure doesn't work very well, despite its compelling themes and characters.
Monday, September 4, 2017
How To Tell A Story With A Video Game (even if you don't make or play games)
This post is a summary of a talk I gave at Storycode NYC on August 22nd, 2017. All the slides are available here. It is a primer for storytelling in games, intended for people who aren't gamers or game developers, but who want to get into interactive storytelling / immersive storytelling (like VR / AR / etc).
Video game design has much to offer interactive designers, even if you don't make or play any video games. When I taught at Parsons, we taught game design as part of our general design / technology curriculum, because this field has been thinking about the aesthetics of digital interaction for literally decades.
So if we want to tell a story with a video game, we should first ask, what is a video game made of? Some men have opinions on this:
Famous game designer Sid Meier has a famous quote: "a game is a series of interesting choices." When we play games, we're constantly making choices and feeding input into the game -- which way should Pac-Man go, how far should Mario jump? Some designers even treat the lack of input as an input. Inaction as an action.
My boss / NYU Game Center director Frank Lantz has a slightly less famous, but much more handsome quote: "a game is an opera made out of bridges." What he means is that a video games often try to present a sort of audio / visual "total work of art" spectacle that demands your complete attention and immersion, but to achieve that bombastic effect we also have to engineer physics simulations and future-proof code bases to work for many years. And if we're going to go with a bridge metaphor, we should also ask, what are these "bricks" and building blocks that make up video games?
Tuesday, August 29, 2017
On the hopeful undead future of VR and "A Short History of the Gaze", by Paolo Pedercini / Molleindustria
I played Paolo Pedercini's first (and maybe last?) virtual reality piece "A Short History of the Gaze" last year at Weird Reality. I think ASHOTG is good for a lot of reasons, but the foremost reason is that few people are making VR art that's critical about VR culture and its politics. The closest we get to is when we twist VR's (faltering?) utopian branding toward our own ends, whether for "empathy machines" or whether for a vision of a "gay VR". But even among artists, it's rare to see VR work that directly critiques what VR is about, in this current moment.
Like a lot of Paolo's other work, it's political and educational, trying to distill critical theory and media studies into a short accessible interactive experience. The player goes on a ~15 minute sequence of different scenes about looking at stuff -- undressing people in an elevator (male gaze), punishing prisoners in a panopticon (incarceral gaze), being trapped by advertising (capitalist gaze), etc. in various situations. I actually found the whole piece to be slightly encouraging, because it positions VR as part of a long tradition of gazes -- and it's also clearly the weakest gaze. If VR is an oppressive force, then that force is currently minuscule or even laughable compared to any other oppressive force in the world.
Which leads us into how VR is doing right now: it doesn't look good for VR.
Thursday, August 24, 2017
Road trip sketches; notes on extracting and visualizing Half-Life 2 levels in Maya
So I'm working on (another) article about level design in Half-Life 2. I chose the d2_coast03 map of the Highway 17 chapter, which is the first real "coastline" road trip section of the game, and is probably the most successful. Look at how big and open it is. Would you believe this is a map in a game celebrated as a meticulous roller-coaster? In my mind, it's contemporary with a lot of vehicle-based first-person open world game design trends that started around the same time in 2004, and they even pulled it off in an engine architecture that's still kinda based on Quake 1.
Thursday, August 17, 2017
Teaching, Fall 2017
As mentioned before, I'm going full-time with NYU Game Center starting this September. For this upcoming fall semester, I'm going to be teaching three classes and advising an independent study:
- Intermediate Game Development (2 sections). This is a required class for the BFA Game Design major where we focus on using Unity in a 3D context, refine C# code fluency, learn about using Maya and Substance Painter, and become less scared of using Git.
This is my fourth year of teaching it. This year, I've changed the final project to focus on studying and cloning a game. In the past, the final project asked students to collaboratively formulate an original game design concept, but I noticed students would get into endless debates about the game design instead of focusing on project architecture or collaboration workflows. Since we already have dedicated game design classes that offer more support for those debates, I now feel comfortable removing some creative freedom from this class -- so we can focus more on building-up "technical freedom." - Intro to VR. This is a new VR-focused class we're running for undergraduates and/or people who aren't so familiar with code and 3D. At Game Center we remain cautious about investing too much in something still fundamentally unproven like VR / AR, but we still want to support students who want to explore it. Unlike our graduate-level VR Studio class which assumes technical proficiency in code and Unity, this class will offer more of a scaffold into working in 3D and VR. We'll also dip our toes into talking about VR culture and critical theory as usual, but probably stop short of discussing Baudrillard and phenomenology.
- Level Design (independent study). Years ago I used to teach a modding class with a level design focus, but one day I noticed students hated using the Source Engine, and we never identified another decent engine / toolset for level design. We also needed a good base game to design more levels for, which is why we can't switch to Source Engine 2 -- DOTA2 isn't exactly relevant for learning generalized level design practices. At least half of our students also use Macbooks, which basically wither and die under Unreal 4, so that's out of our reach too.
But then a few months ago, some students approached me to advise an independent study on level design. This format is more like a seminar / reading group instead of a full production-oriented studio class, and we will focus more on theory than construction. Hopefully this will work out better than the Source modding class!
Tuesday, August 15, 2017
StoryCode August 2017 Forum at Film Society, Lincoln Center, NYC

Next week on August 22nd, I'll be giving a presentation for StoryCode, a local community group focused on immersive media and storytelling technology. As one of the few game designers invited to present in their lecture series, I thought I'd try to explain how video games conceptualize narrative, interaction, and expression, to an audience that maybe doesn't play that many video games -- or at least, they don't play what we consider to be the state-of-the-art narrative games.
I'm also being required to talk about my games and present them as case studies, even though my games don't fit neatly into the "narrative game" genre. I think I'll probably just open my actual project scenes in the Unity editor and mess with my scene setup and code, which usually entertains people well-enough? It'll also be a short primer in foundational ideas like immersive fallacy / procedural rhetoric / platform studies, and the idea that production value and paratext amount to their own kind of "story."
The presentation is free and open to the public, but I believe you're encouraged to sign-up and RSVP via this Meetup page or something.
Tuesday, August 22, 2017 @ 7:00 PM
Elinor Bunin Munroe Film Center @ Film Society of Lincoln Center
144 West 65th Street, New York, NY (map)
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)




